The chemical notation HCOOCH CH2 H2O presents a fascinating puzzle for students and chemists alike. While it doesn’t represent a single stable compound, it points toward a mixture involving specific reactants and products in an aqueous environment. Understanding this notation is key to unlocking the principles of ester hydrolysis and related organic reactions. It signifies the interaction between an ester, specifically methyl formate (HCOOCH3), and water (H2O), with CH2 likely representing an intermediate or a related component in a broader chemical context.
What is HCOOCH CH2 H2O?
At its core, the notation HCOOCH CH2 H2O describes a chemical system rather than a distinct molecule. It implies the presence of methyl formate (HCOOCH3) and water (H2O). The “CH2” component is less straightforward but often refers to a methylene group, which could be part of a reactant, an intermediate like a carbene, or a byproduct in a more complex reaction scheme. Therefore, we interpret this as a reaction mixture where methyl formate interacts with water.
The Role of Methyl Formate (HCOOCH3)
Methyl formate is the simplest carboxylic ester. It’s a colorless liquid with an ethereal, pleasant odor. In the context of HCOOCH CH2 H2O, it is the primary organic substrate undergoing a chemical transformation.
The Significance of Water (H2O)
Water acts as a reactant and the solvent in this system. Its presence is crucial for the hydrolysis reaction to occur, where it breaks the ester bond.
Interpreting the “CH2” Component
The “CH2” or methylene group’s role can vary. It might be part of a larger reactant molecule not fully specified, or it could represent a highly reactive intermediate formed during the reaction. In many educational contexts, it simplifies a more complex structure involved in the synthesis or reaction of the primary ester.
How HCOOCH CH2 H2O Works: The Mechanism
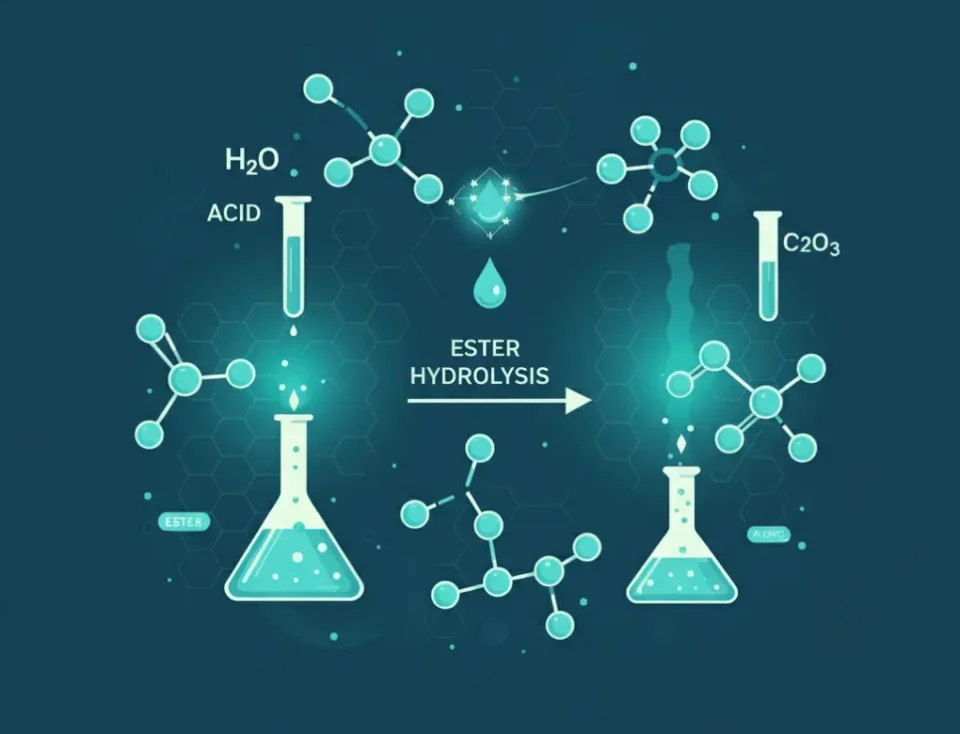
The primary interaction in a system described as HCOOCH CH2 H2O is ester hydrolysis. This process is fundamental to organic chemistry and involves breaking down an ester into its constituent carboxylic acid and alcohol. The overall process can be catalyzed by either an acid or a base, significantly affecting the reaction rate and mechanism.
The general principle of how hcooch ch2 h2o works is through nucleophilic acyl substitution. The water molecule acts as a nucleophile, attacking the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of the methyl formate. This initiates a sequence of steps leading to the cleavage of the ester linkage.
The HCOOCH CH2 H2O Chemical Reaction
The key hcooch ch2 h2o chemical reaction is the hydrolysis of methyl formate. This reaction breaks the ester bond (COO) using a water molecule. The result is the formation of formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol (CH3OH). The balanced chemical equation for this hydrolysis is:
HCOOCH3 + H2O ⇌ HCOOH + CH3OH
This reaction is reversible. The forward reaction is hydrolysis, and the reverse is esterification (Fischer esterification), where an acid and an alcohol combine to form an ester and water. The direction of the equilibrium depends on the reaction conditions, such as the concentration of reactants and the removal of products.
Factors Influencing the Reaction Rate
Several factors can influence the speed of the hcooch ch2 h2o chemical reaction:
- Temperature: Increasing the temperature generally accelerates the reaction rate by providing molecules with more kinetic energy.
- Catalyst: The presence of a strong acid (like H2SO4) or a strong base (like NaOH) significantly speeds up hydrolysis.
- Concentration: Le Châtelier’s principle applies here; for instance, using a large excess of water will push the equilibrium toward the products (formic acid and methanol).
Applications and Industrial Relevance
While the specific notation HCOOCH CH2 H2O is primarily educational, the components are industrially significant. Understanding their interactions is crucial in various fields. Methyl formate itself has several important uses.
- Fumigant and Larvicide: It is used to control pests on dried fruit, tobacco, and other stored goods due to its high volatility and effectiveness.
- Industrial Solvent: It serves as a solvent for various polymers and resins in manufacturing processes.
- Chemical Intermediate: It is a precursor in the synthesis of other important chemicals, including formic acid and formamides.
Hydrolysis reactions are also central to many biological and industrial processes, from the digestion of fats in the body to the production of soaps (saponification).
Safety Considerations and Lab Practices
When working with the components suggested by HCOOCH CH2 H2O, proper safety protocols are essential. Methyl formate is highly flammable and has a low flash point.
- Ventilation: Always handle methyl formate in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to avoid inhaling the vapors, which can cause irritation.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear safety goggles, gloves, and a lab coat to protect against skin and eye contact.
- Fire Safety: Keep methyl formate away from open flames, sparks, and other ignition sources. Have appropriate fire-extinguishing equipment (like a CO2 or dry chemical extinguisher) readily available.
- Storage: Store containers of methyl formate tightly sealed in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated location away from oxidizing agents and acids.
Following these guidelines ensures that any experiment involving the hcooch ch2 h2o chemical reaction is conducted safely and effectively.
Conclusion: A System of Interaction
The term HCOOCH CH2 H2O is best understood not as a single compound but as a description of a chemical system. It points to the hydrolysis of methyl formate in water, a fundamental reaction in organic chemistry. This interaction yields formic acid and methanol, with the “CH2” fragment representing a contextual part of a broader reaction. By breaking down the notation, we gain insight into the principles of ester chemistry, reaction mechanisms, and the importance of laboratory safety. This exploration serves as a valuable exercise in chemical interpretation and problem-solving.
FAQs
1. What does HCOOCH CH2 H2O mean in simple terms?
It represents a chemical mixture where methyl formate (HCOOCH3) reacts with water (H2O). The “CH2” is a contextual placeholder for a methylene group involved in the reaction.
2. What is the primary chemical reaction involved?
The main reaction is the hydrolysis of the ester, methyl formate. This reaction uses water to break the ester down into formic acid and methanol.
3. Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O a stable compound?
No, it is not a single, stable compound. It is a notation used to describe a system of reacting chemicals in an aqueous solution.
4. Why is a catalyst often used for this reaction?
A catalyst, such as an acid or base, is used to speed up the rate of hydrolysis. Without a catalyst, the reaction between an ester and water is typically very slow.
5. What are the products of the hcooch ch2 h2o chemical reaction?
The primary products from the hydrolysis of methyl formate (HCOOCH3) with water (H2O) are formic acid (HCOOH) and methanol (CH3OH).
For more info please visit prothots